Lake Flores Brings New Urbanism to Southwest Florida
“A positive example of change,” “the right development at the right time,” and “a life-preserver” were just a few of the positive comments heard during August’s Manatee County Commission meeting to review the Lake Flores project. At the meeting, Commissioners unanimously approved the initial development plan for Lake Flores.
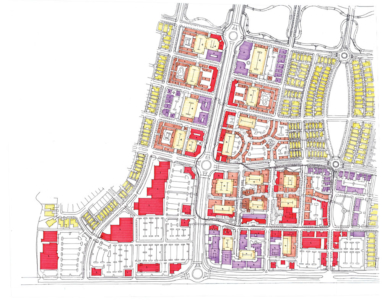
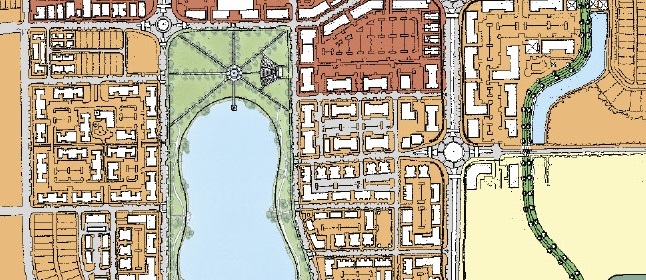
As a result, over 1,300 acres of farmland surrounded by existing suburban development in west Manatee County will come back to life as the mixed-use residential infill community of Lake Flores. “This is the best thing since Lakewood Ranch,” said one of the participants at the meeting, unknowingly citing another project in Manatee County designed by Canin Associates. Begun in 1995, Lakewood Ranch is a successful 17,500-acre master-planned community.
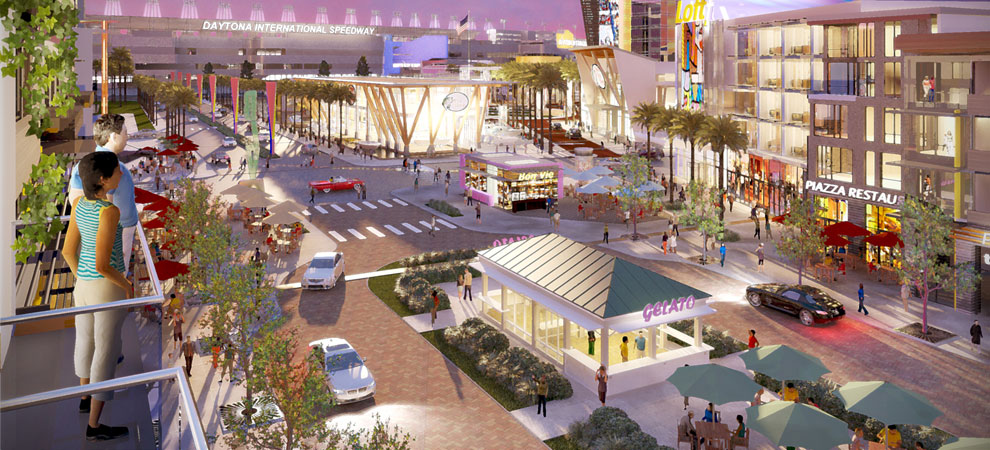
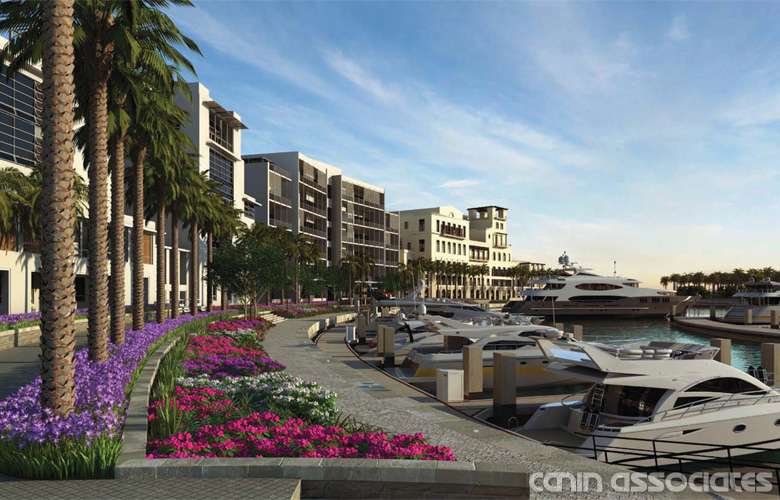
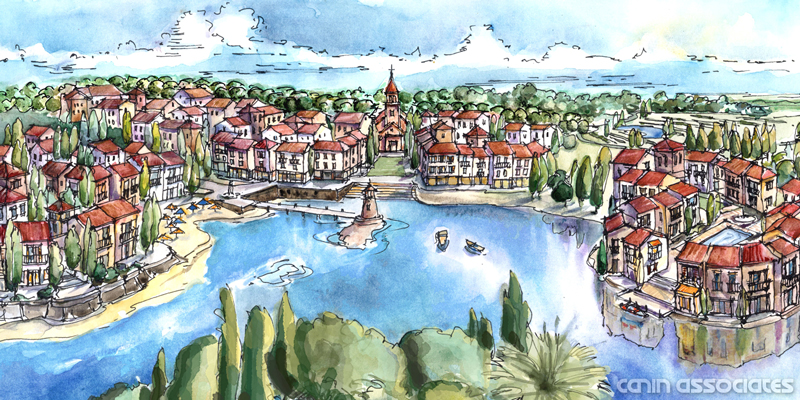
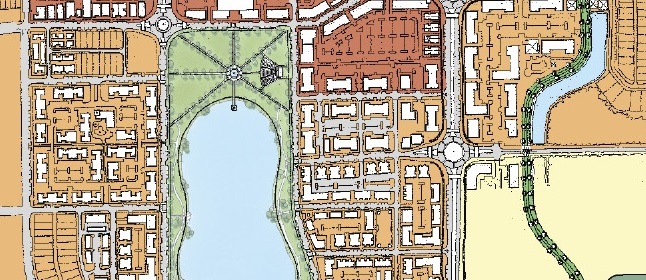
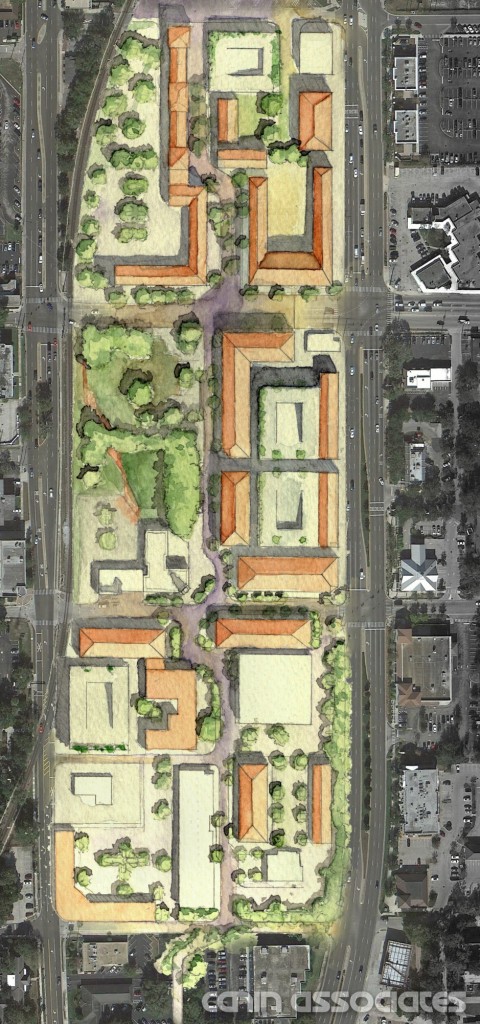
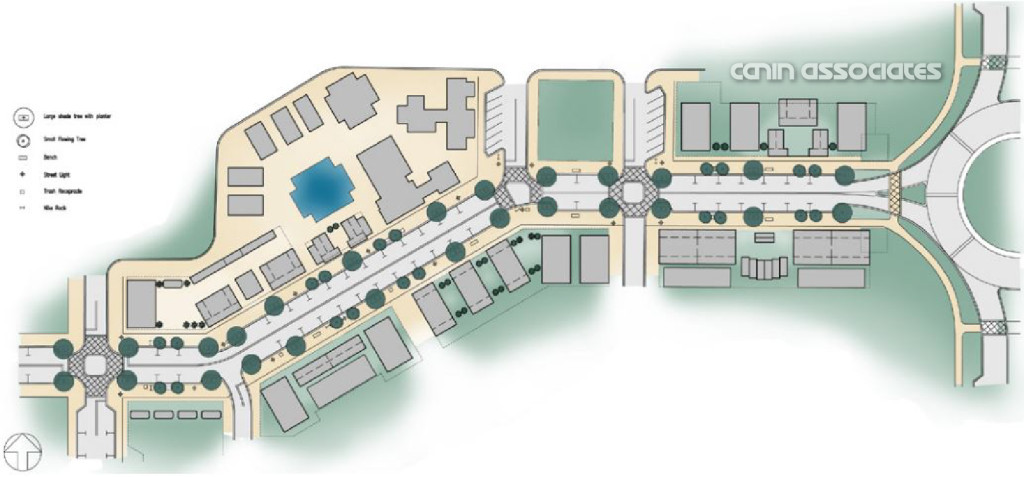
The heart of Lake Flores will be the 19-acre namesake lake and its surrounding urban park. Interlaced with these greenspaces are community areas, events spaces, and a new Main Street that will be home to restaurants, shops, and entertainment. During its 20-year buildout, Lake Flores is set to grow into bustling, walkable neighborhoods with 6,500 residential units, 3 million square feet of commercial and retail space, and 500 hotel rooms.
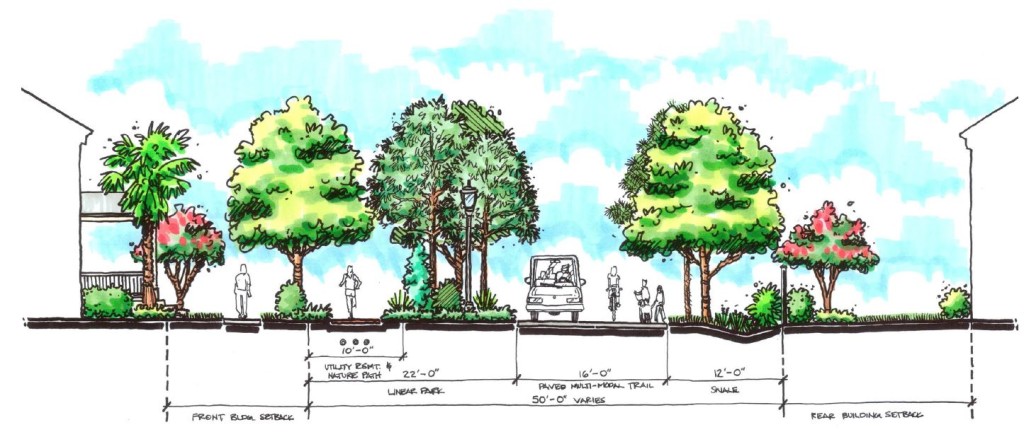
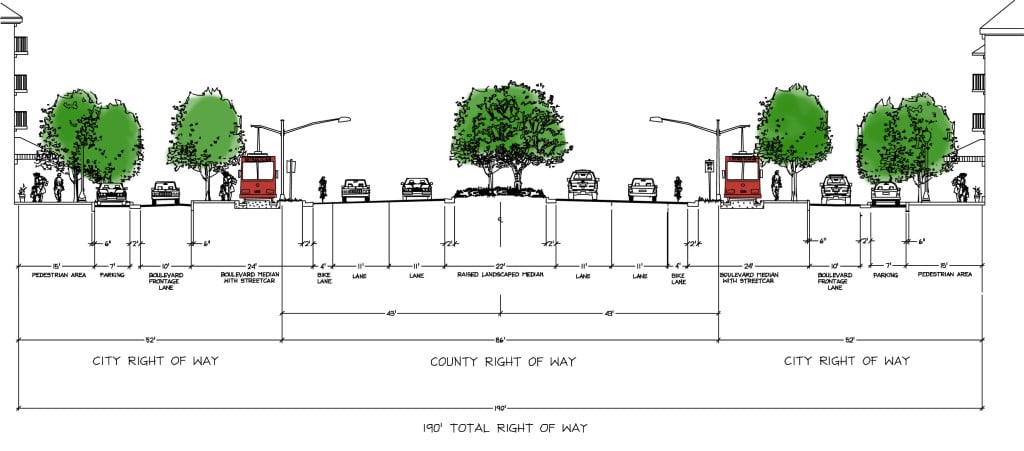
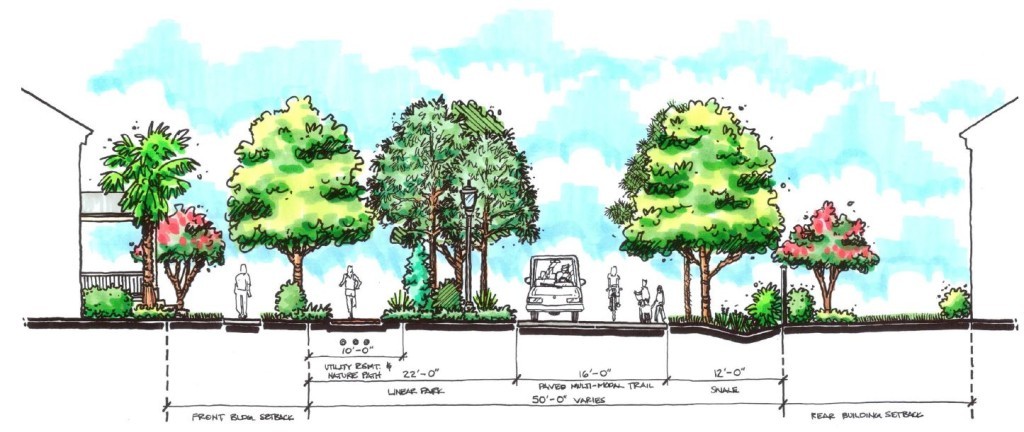
As a true mixed-use community, Lake Flores will offer a variety of housing options and a transportation system that supports a diversity of users. Apartments overlooking Lake Flores will create a peaceful yet urban residential option for young professionals while master-planned neighborhoods will focus on innovative single-family housing types. Meanwhile, the streets and multi-use trail system will move more than cars: people on foot, on bike, and in small electric vehicles will be able to explore Lake Flores conveniently and safely.
“From an economic standpoint, this is very positive for Manatee County and the area,” Lake Flores property owner and lifelong area resident Whiting Preston told the Bradenton Herald. Not only will the development attract newcomers to the area, but current residents—especially young adults looking to buy their first homes—will be able to stay in Bradenton due to the array of housing choices. This notion is underscored by two distinct business centers which will promote job growth in the commercial, research, and development sectors.
Lake Flores is poised to reignite Bradenton and west Manatee County as a very special place to live. As an infill community, Lake Flores will provide housing and retail/office space in a location where it is needed. As a mixed-use, traditional neighborhood, Lake Flores will grow into a walkable, New Urban addition to the region that will be attractive to Millennials, families, and retirees.